Are most businesses actually having a Data Swamp or a Data Lake?
The concept of a business or organization having data lakes has been in existence for many years now. The term data lake wasn’t part of any traditional data-storage architecture, so vendors freely used it to mean many different things.
But what happens if the data is not properly maintained? This article will explain what exactly a data swamp is and how you can avoid having one.
Introduction to Data Lake
A data lake is a centralized data storage that can store different data types from structured data to unstructured data. As the amount of data in a company or business grows exponentially, the data must be stored somewhere.
Data Lake is an approach to Big Data architecture that focuses on storing unstructured, structured, and semi-structured data in a single repository
Data lakes can store the data in a native format, without the need for limits or storage restrictions. It can store relational data from business applications while also able to store non-relational data from mobile apps, IoT devices, and social media.
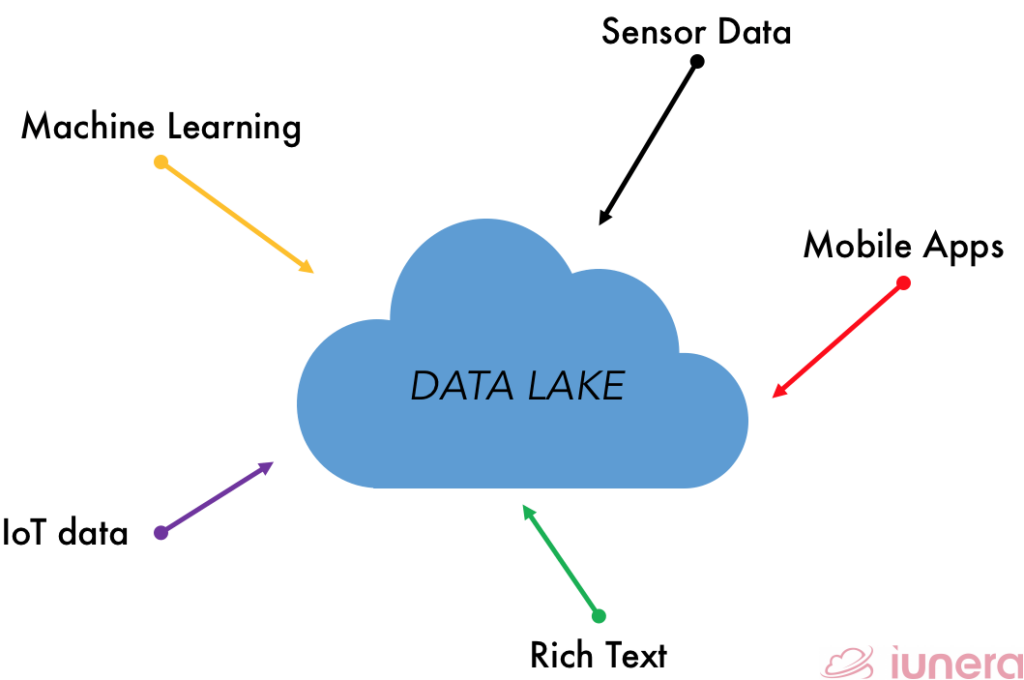
Importance of Data Lakes
There are a couple of reasons why incorporating a data lake storage is important to organizations. Listed below are some of the reasons why a data lake is important and useful.
1. A proper data storage
With the recent increase of unstructured and structured data, analyzing data becomes a mess without a standardized system or model. A data lake can transform the business by providing a singular repository of all the organization’s data.
2. Organise data effectively
Data lake analogy will help bring a common understanding of the benefits of distributed computing systems that can handle multiple types of data, in their native formats, with a high degree of flexibility and scalability. All of this starts with organizing the data effectively.
3. Improve data handling and analytics
If an organization does analytics with IoT or sensor data, a Data lake will definitely make it easy to store and run analytics on machine-generated data to discover ways to reduce operational costs, increase analytical intelligence with Machine Learning and overall quality.
What is Data Swamp?
Data lakes always start out with good intentions, but sometimes they take a wrong turn and end up as data swamps. A data swamp is a data pond that has grown to the size of a data lake but failed to attract a wide analyst community, usually due to a lack of self-service and governance facilities.
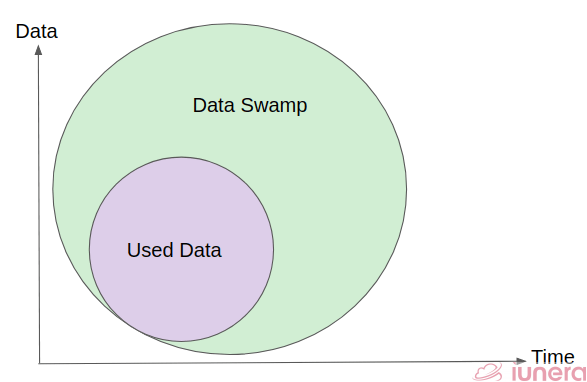
Often times, the data in the data swamp are used in smaller batches and are either properly maintained or not maintained at all. When the data is not maintained, it is left out to accumulate, which is why data swamps are created.
Data lakes, in the absence of ongoing maintenance, will inevitably become swamps, unusable, and unhelpful to your organization.
By Bob Whelan
When data lakes first came onto the scene, a lot of companies rushed out to buy Hadoop clusters and fill them with raw data, without a clear understanding of how it would be utilized. This led to the creation of massive data swamps with millions of files containing petabytes of data and no way to make sense of that data since it is not serviced or used.
How do you check if you have a Data Lake or Data Swamp – 5 Things
Though data lakes are often constructed without proper data context, governance controls, and speed to evolve at the same rate, the business consumes the data. To effectively build and maintain a data lake requires taking advantage of digital insight with strategic planning, advanced technical skills and knowledge, and proper digital maintenance.
Below are some guides that you can follow to ensure that the current data that you have in your organization is not left out to be a data swamp:
1. Information – Understand the data
Data understanding is the foundation on which every automated business process depends. The ability to understand what types of data needed to be collected is crucial when it comes to making successful informed decisions. Knowing where, when, how and by whom any data was created is just as critical as what that data represents.
2. Metadata – Label your Data
Metadata is your way of describing and categorizing data. Examples of different types used today include descriptive metadata, structural metadata, and administrative metadata.
In the absence of metadata, organizations wind up with a massive amount of largely unusable data that has little to no value for the business because nobody can find it. It then becomes unusable and if not managed properly, grows into the data swamp.
3. Mapping – Connecting your data to everything
Data mapping establishes the relationships between the data sets. Once data sets are mapped, it becomes possible to create the data model with proper links and connections such that none of the data is lost in the matrix. And with proper mapping, the history of the data can be understood as well.
4. Maintenance – Data has to be serviced
Data lakes do not magically maintain themselves. New types of data are being added at such a high rate that some regulations and maintenance are required.
Sometimes, data often needs to be moved from one location to another. These things can only be done if the data is properly maintained.
5. Meaning – What kind of data

When organisations and companies collect the data, they could find that what was once a well-organised data lake is now a data swamp flooded with the information they may never need. This mindset must be avoided to prevent having too much irrelevant data in the data lake that is not useful at all.
Leaders of companies should also adopt future-oriented mindsets data collection. But, when doing that, they must be careful not to fall into the trap of gathering data “just in case.” Making clearly defined goals about data usage helps prevent over-eagerness when collecting the information.
In Summary
Building an efficient data lake system is not just about the data – it’s about what the data lake can offer to other parties. Data lake creates a unique platform where we have the ability to apply a structure on varied datasets in the same repository.
But when the data is left unmaintained, it becomes a data swamp. Data swamps in any organization are not useful as they bloat up the storage space, wasting money and time of the people who need to maintain it.
Are you looking for ways to get the best out of your data?
If yes, then let us help you use your data.
FAQ
What is actually a Data Swamp?
A data swamp is a data pond that has grown to the size of a data lake but failed to attract a wide analyst community, usually due to a lack of self-service and governance facilities
How to prevent a Data Swamp?
What is a Data Lake?

A data lake is a centralized repository or database that can store different data types from structured data to unstructured data


