In every business or organization, Data is fundamental to its decisions. A company’s ability to gather the right data, interpret it, and act on those insights is often what will decide its level of success. Business data can come from many different sources such as IoT, media, tweets, financial data, documents, etc. These kinds of data can be divided into Structured and Unstructured data.
This article will take a closer look at the meaning and differences between Structured, Unstructured, and finally Semi-Structured Data.
Introduction
Over the past decade, it is apparent that properly analyzed data drives the modern organization – making sense of this data becomes critical and a hugely rewarding endeavor.
Immense data streams from various origins help businesses to make important data-driven decisions, upscale profits, and to harness new opportunities as well as present itself as an improved way to strategize for organizations regardless of their size or market value.
Data can come in many different formats ranging from as simple as time series data to as complex as real-time financial transactions.
Processed data is information. The processed information is knowledge; Processed knowledge is wisdom.”
Ankala V. Subbarao
Moreover, data can be generated in many ways. The data sources can originate from first, second, or third-party data. First-party data is the data you collect directly from your audience. Second-party data is the data you buy from a partner company that collects from its audience. Third-party data is mainly data collected from various data owners by an aggregator and sold as a packaged data set.
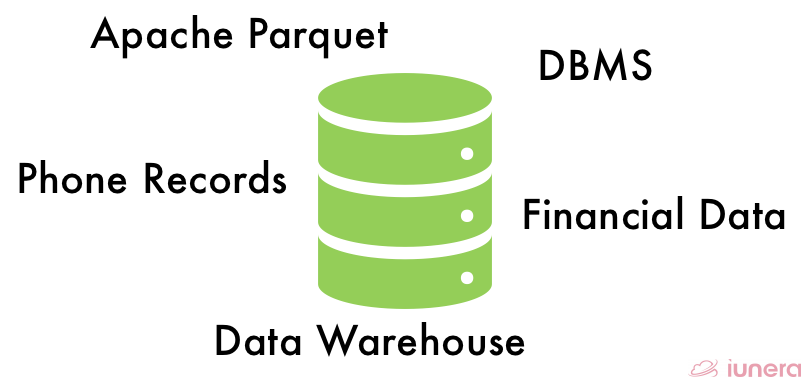
What is Structured Data?
A database allows multiple users to maintain, update, and edit stored information quickly, securely, and efficiently. For example, an online directory uses a database to store people’s data, phone numbers, location, address, and others. A database stores rich text and numbers accordingly that can be accessed and searched effectively. This is called structured data.
Structured data are the types of data that are in a standardized format for providing information about something. Structured data are always predefined, so analyzing it would be trivial. Moreover, structured data has finite attributes – hence we know what kind of elements would be present in the data.
Structured data is typically stored in a relational database (RDBMS). Structured data is managed using Structured Query Language (SQL), a programming software language developed by IBM in the 1970s for relational databases.
It is currently being used as a database management language that offers a highly organized and structured approach to information management. At most, structured data will always conform to a tabular format in Rows and Columns which can be sorted and queried.
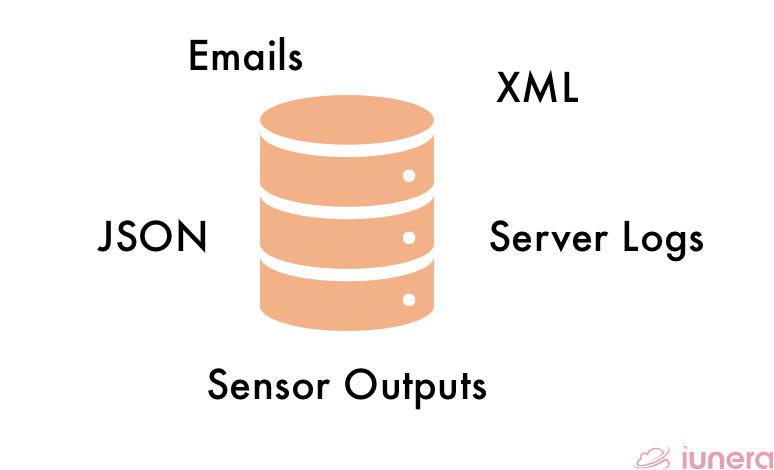
What is Semi-Structured Data?
Semi-structured data are the types of data that are based on Extensible Markup Language (XML). Semi-structured data does not contain the same level of flexibility as structured data. In addition to XML, HTML is a subset of XML since most parts of an HTML in extendable – meaning only a part of the structure is understandable.
The data that is considered semi-structured does not reside in fixed fields or records but does contain elements that can separate the data into various hierarchies.
A typical example of semi-structured data is photos taken with a smartphone. Every photo contains some mixture of semi-structured image content as well as the time, location, and other identifiable information.
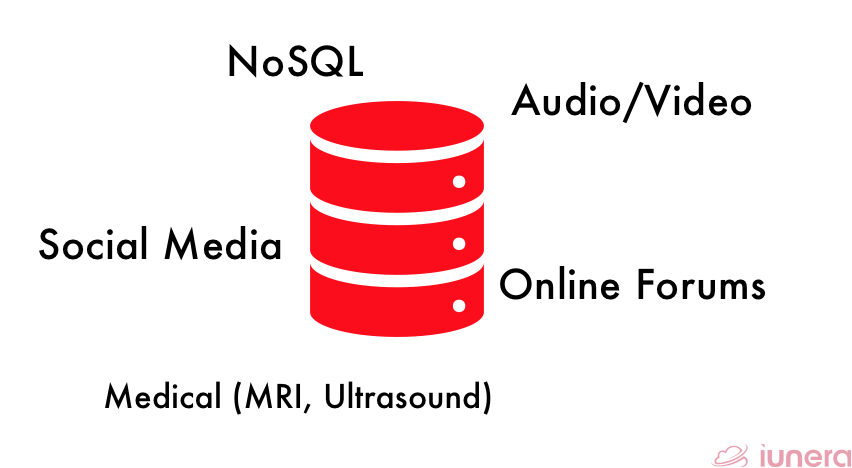
What is Unstructured Data?
Unstructured data are more or less data that does not have a structure or data that is not within the semantics of rows and columns. In the modern world, abundant unstructured data are arising from sensors readings, IoT applications, text data, and many more.
Unstructured data has an internal structure, but it’s not predefined through data models. These types of data might be human or machine-generated in a non-textual format.
In a simple sense, unstructured data can be thought of as data that is not managed in a relational database management system (RDBMS). For example, most radiological report data are only available as unstructured narrative text in the medical field.
Currently, major hospitals have adopted and are providing vendor-neutral reporting, which generates technical details for interoperable, standardized, and structured report templates for doctors and physicians’ ease.
Nevertheless, the integration of structured radiology reporting is still an issue or scarce in the clinical world.
Examples of Data
Currently, there are many different types of data revolving around us, whether we are aware of it. Different sources of data can be categorized into structured or unstructured data.
Structured Data
Semi Structured Data
Unstructured Data
Comparison of different Data Types
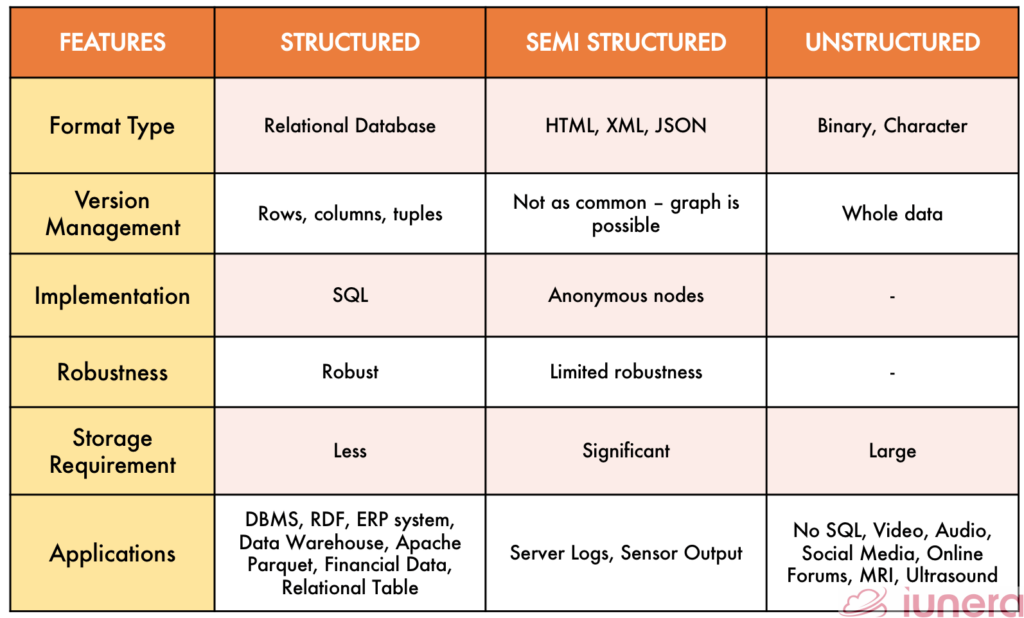
Summary
In every business or organization, there will be access to massive amounts of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data from different sources in all formats. To make use of the data, robust data analytics must be performed to make the most of the data. Separating the data accordingly to its types is the first step to performing analysis.
To recap, structured data is easily organizable, which follows a rigid format; unstructured is complex. Often times, highly qualitative information is impossible to reduce to or organize in a relational database, and semi-structured data has both elements.
Are you looking for ways to get the best out of your data?
If yes, then let us help you use your data.
What is a Structured Data?
What is a Semi-Structured Data?
What is an Unstructured Data?
What is the difference between Structured and Unstructured Data?
Structured data are the types of data that are in a standardized format with the presence of a database with at minimum rows and columns whereas unstructured data are more or less data that does not have a structure
What are some examples of Unstructured Data?
Some of the examples of unstructured data are Audio/Video files, NoSQL, Medical (MRI, Ultrasound), Social Media